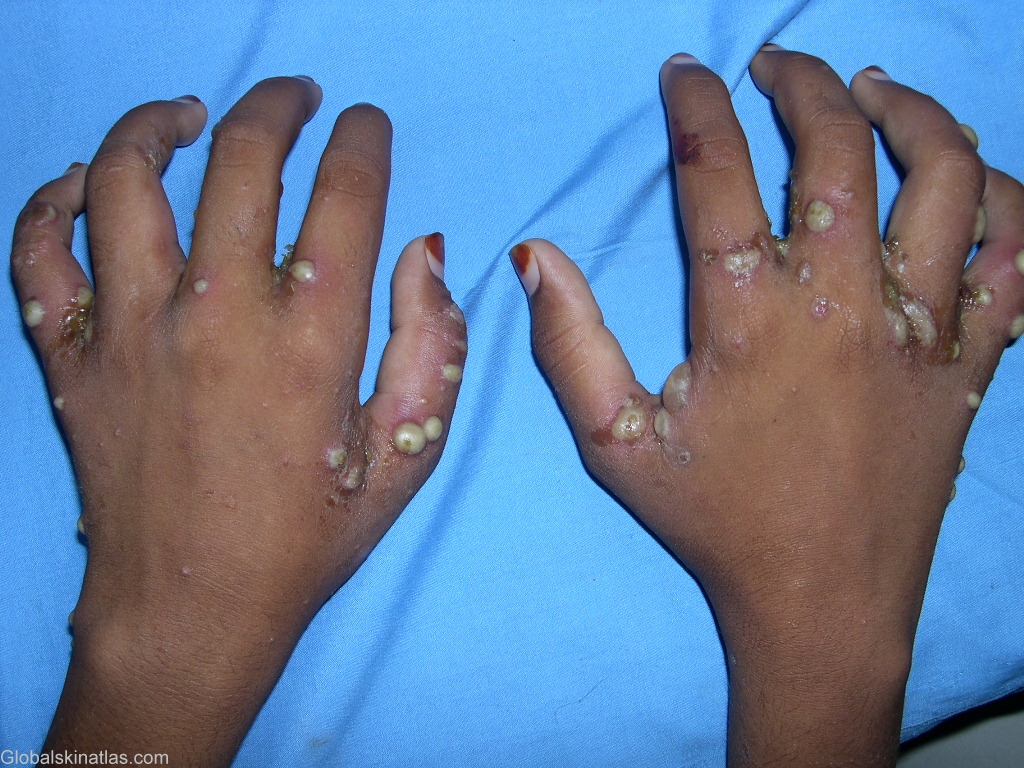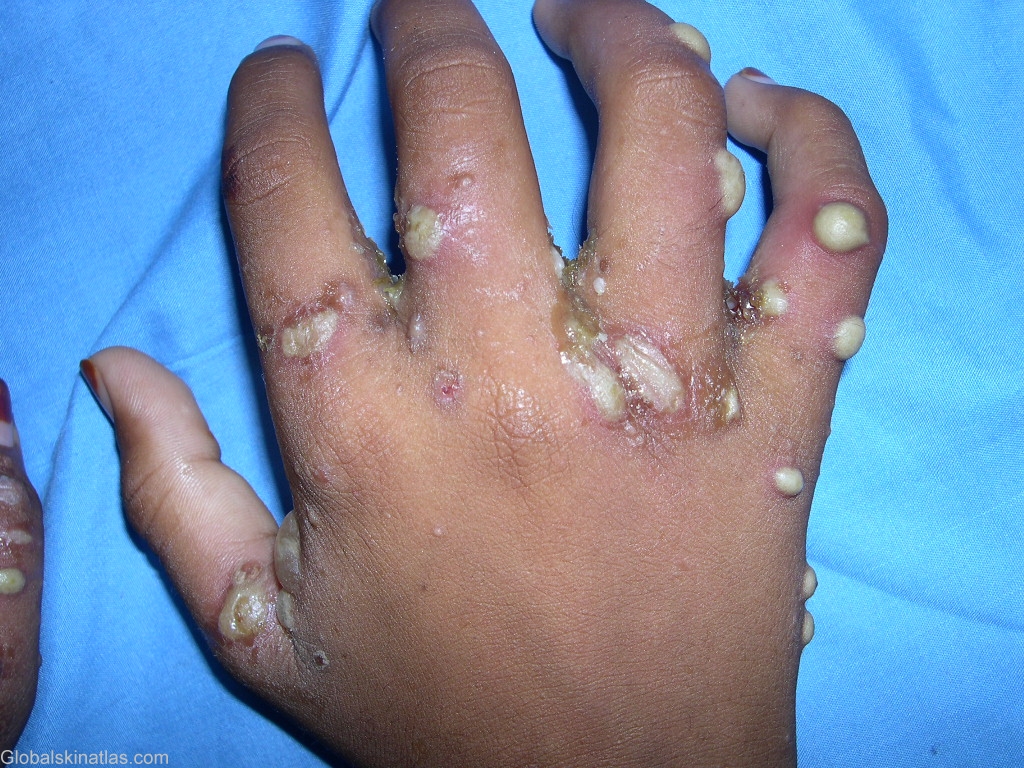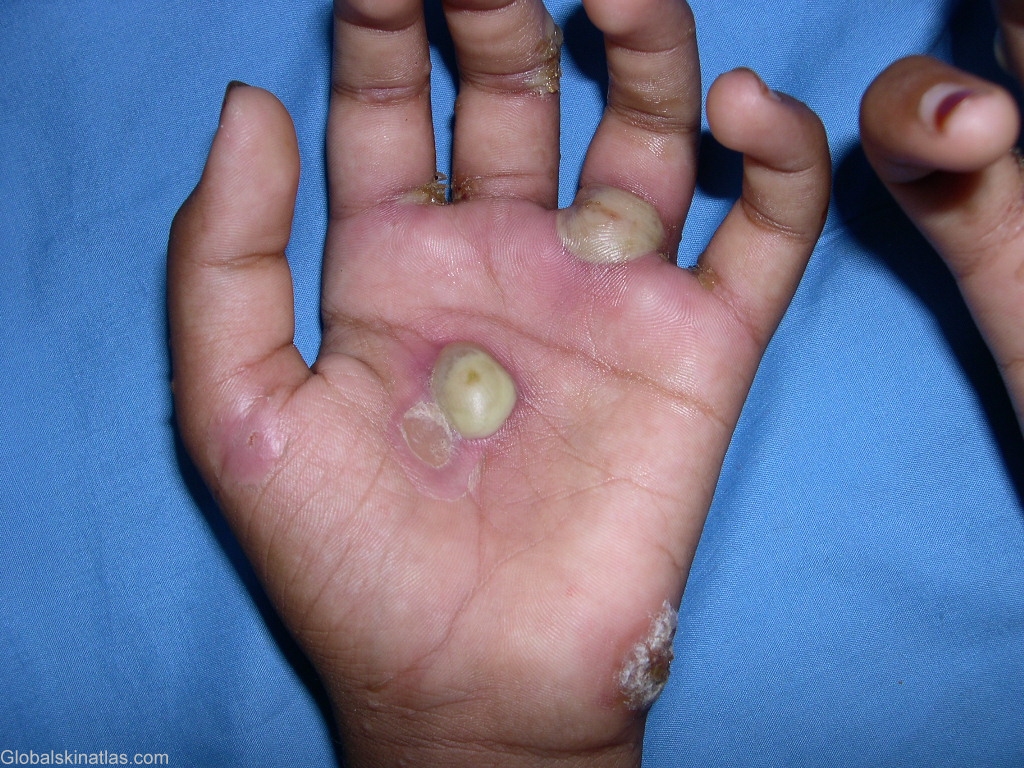
Diagnosis: Scabies
Description: Superaded staphylococcal infection of the lesions of scabies
Morphology: Pustules
Site: Hand,palm
Sex: M
Age: 5
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Shahbaz Janjua
Differential DiagnosisHistory: Scabies is characterized by an intense pruritic papular eruption, superficial burrows, excoriations and secondary infection. It is caused by the highly contagious mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which is an obligate human ectoparasite.
Most patients complain of intense pruritus (particularly at night and following a hot shower), which has been associated with a hypersensitivity reaction to excreta deposited within the burrow. Lesions are generally symmetrically distributed and usually spare the face and neck. These include small papules and vesicles, often accompanied by plaques, pustules, or nodules. The pathognomonic sign of scabies is the presence of multiple burrows on the skin, typically located in the interdigital web spaces, flexural aspects of the wrist and elbows, belt line and genitals. The burrow appears as a fine, wavy, and slightly scaly line 0.2-mm to 1-cm long. A tiny mite is often visible at one end of the burrow. Although the patient may have hundreds of itching papules, often there are less than 10 burrows. Secondary lesions include papular excoriations, scaly eczematoid patches, and red-brown nodules and vesiculopustules. The burrow is often found surrounded by infiltrates of eosinophils, lymphocytes and histiocytes on histopathology.