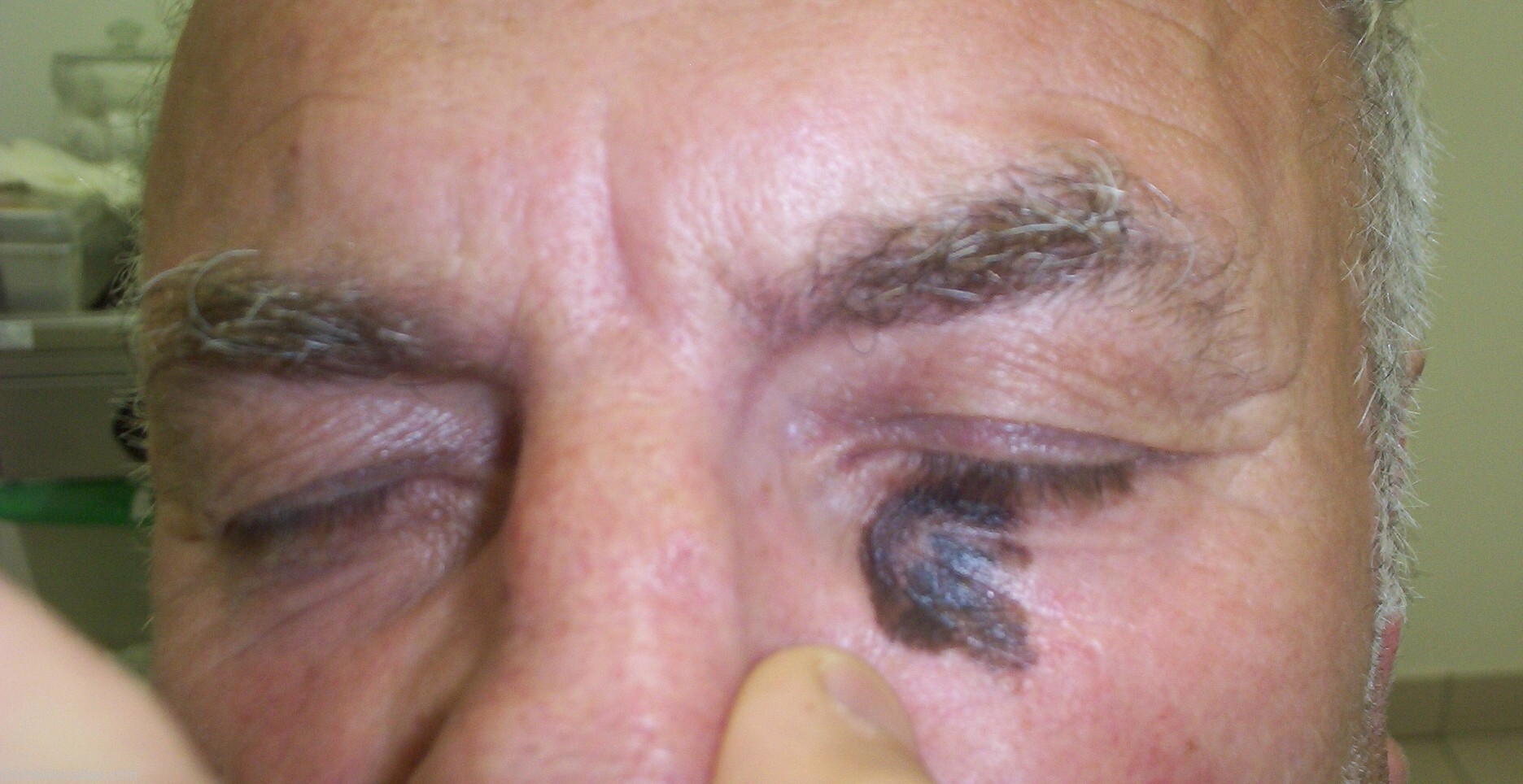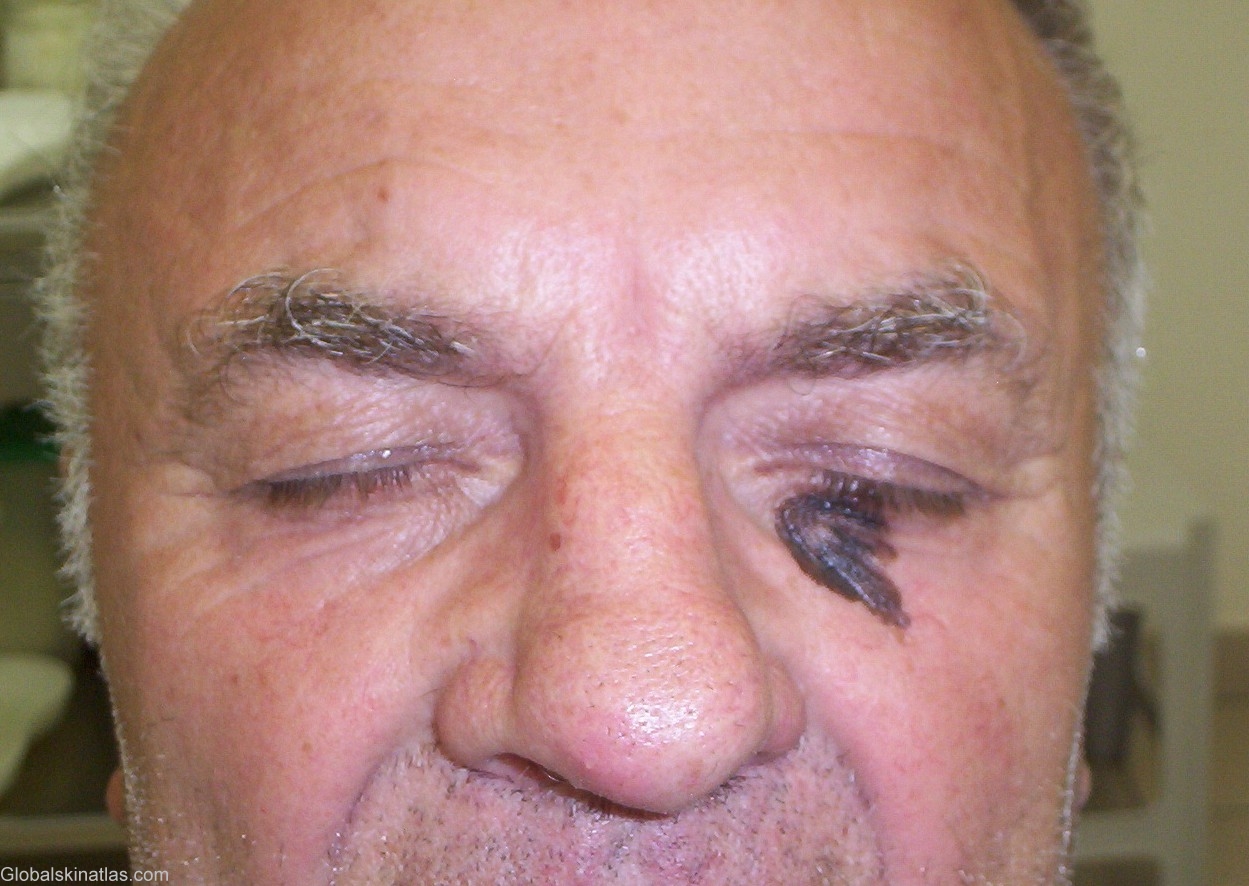
Diagnosis: Melanoma
Description: Asymmetrical heavily pigmented patch with a small papule upon it, irregular borders, and an uneven surface.
Morphology: Path,tumour
Site: Face
Sex: M
Age: 63
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Mehravaran Mehrdad
Differential DiagnosisHistory: Melanoma There are four recognized clinicohistologic classic types of melanoma: 1. Lenitigo maligna (melanoma in situ, noninvasive melanoma). 2. Superficially spreading melanoma (superficial spreading melanoma) 3. Nodular melanoma 4. Acral-lentiginous melanoma. Superficially Spreading Melanoma (SSM) This is commonly called superficial spreading melanoma, the commonest type of melanoma, constituting 70% of them. It affects adults of all ages, with the median age of 5th decade. The upper back of both sexes and the shins in women are the commonest sites. It may occur anywhere, however. It tends to be multicolored, not just with different shades of tan, but variegated black, red, brown, blue and white. The border is often notched by focal regression or asymmetric growth. As the vertical growth phase develops, skin markings disappear. If regression occurs, these may disappear. These lesions grow as much in a year as lentigo maligna does in three to five years. Easy bleeding is a sign of malignancy, as is erosion or ulceration. Horizontal or lateral growth into the adjoining epidermis continues for one to five years, before invasion into the dermis take place. A 63-year-old man with chief complaint of asymmetrical patch with a small papule upon it, irregular borders, heavily pigmented and an uneven surface. ABCDs were very typical for SSM. Patient was transfered to the regional melanoma center in Szeged for further management which includes in toto excision with saftey margin, staging, and further treatment.