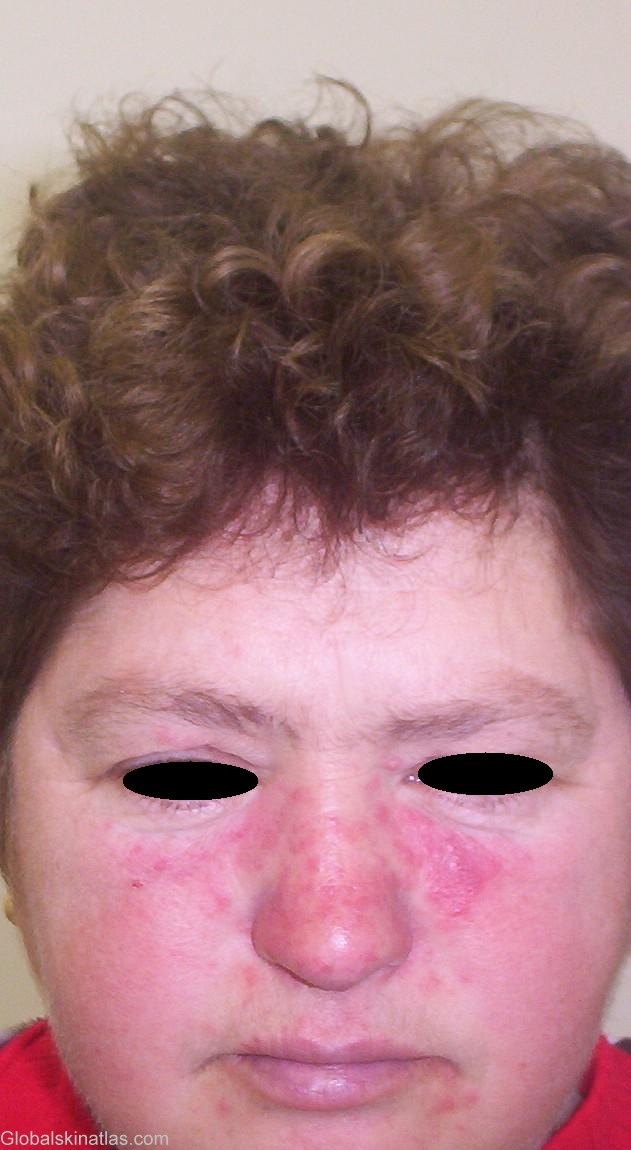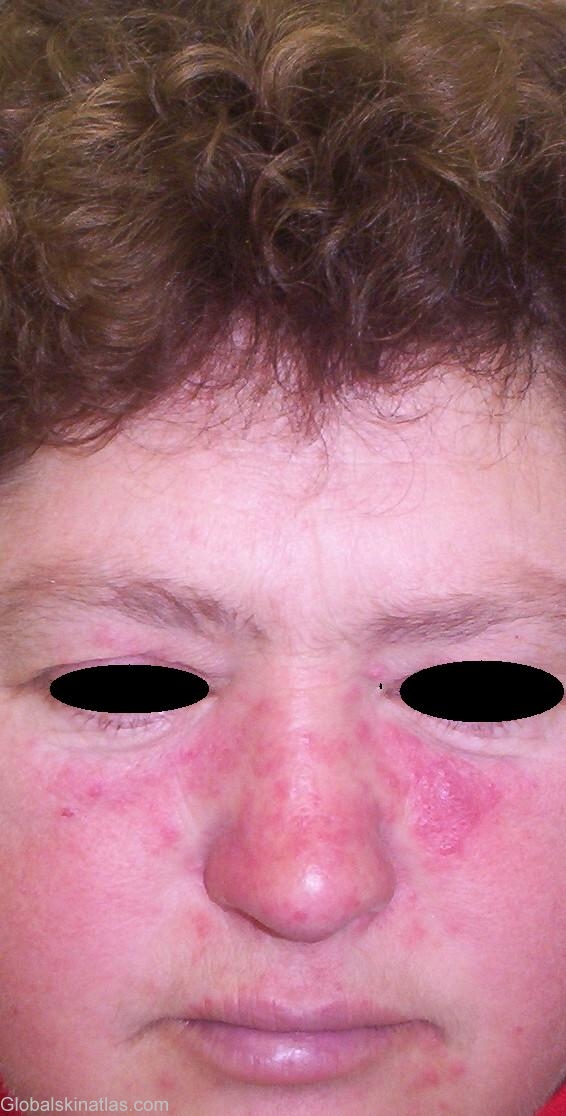
Diagnosis: Rosacea
Description: Papules and pustules in the mid-face (nasolabial regions)
Morphology: Plaque
Site: Face papules multiple
Sex: F
Age: 52
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Mehravaran Mehrdad
Differential DiagnosisHistory:
Rosacea, also called acne rosacea, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition familiar to all dermatologists. Rosacea is charaterized by four stages of pathologic events. The sequence is not obligatory, and few patients complete the full course of the disease, its progress in most cases being arrested in the second atage. The frequent episodes of flushing (first stage) are followed by persistent erythema telangiectasia (second stage). Only a small number of these patients develop papaules and pustules (acne rosacea). The last stage includes rhinophyma and hyperplasia of nasal sebaceous glands which are seen mostly in affected male patients. Rosacea is mainly seen in 40-60 years old women and concominant occular involvement may occur in up to 58% of patients. There is a strong correlation between the degree of eye involvement and tendency to flushing. This may take the form of belpharitis, conjunctivitis, episcleritis, iritis and keratitis.. Other associated complaints include gastrointestinal upset and migrane headache.
This 52-year old female appears with the chief complaint of centro-facial papulo-pustular plaques. Treatment with metronidazole (Klion®) 250mg twice a day for 3 weeks with combination topical agents (mild corticosteroid, sulfur powder in an emollient base) achived a satisfactory recovery in 5 weeks. Patients should also be prohibited from exacerbating factors such emotional stress, sunlight, wind, hot beverages, spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, and extermes of heat and cold. Search for Helicobater pylori usually reveal an negative result.