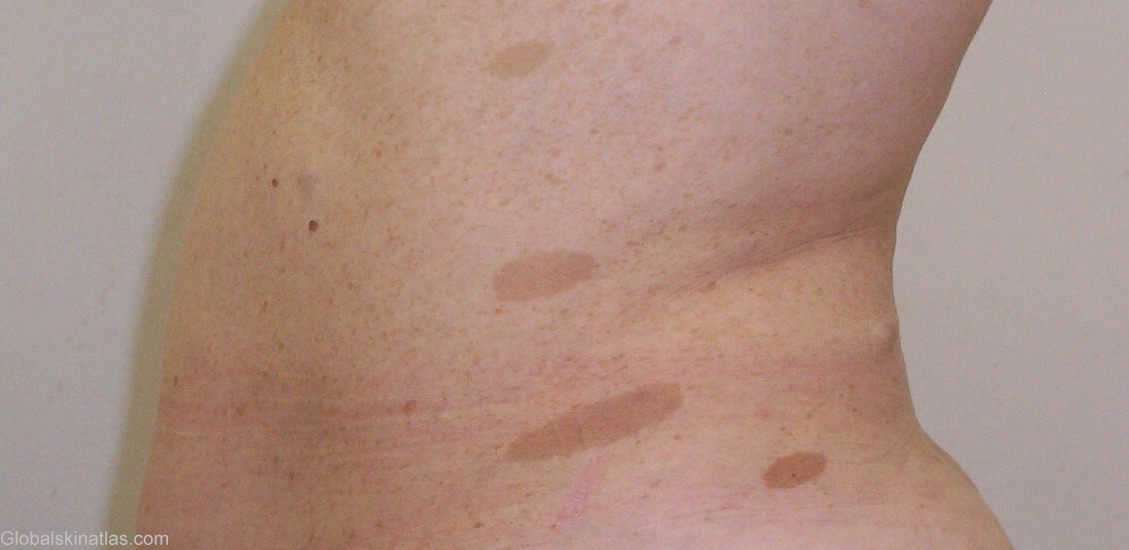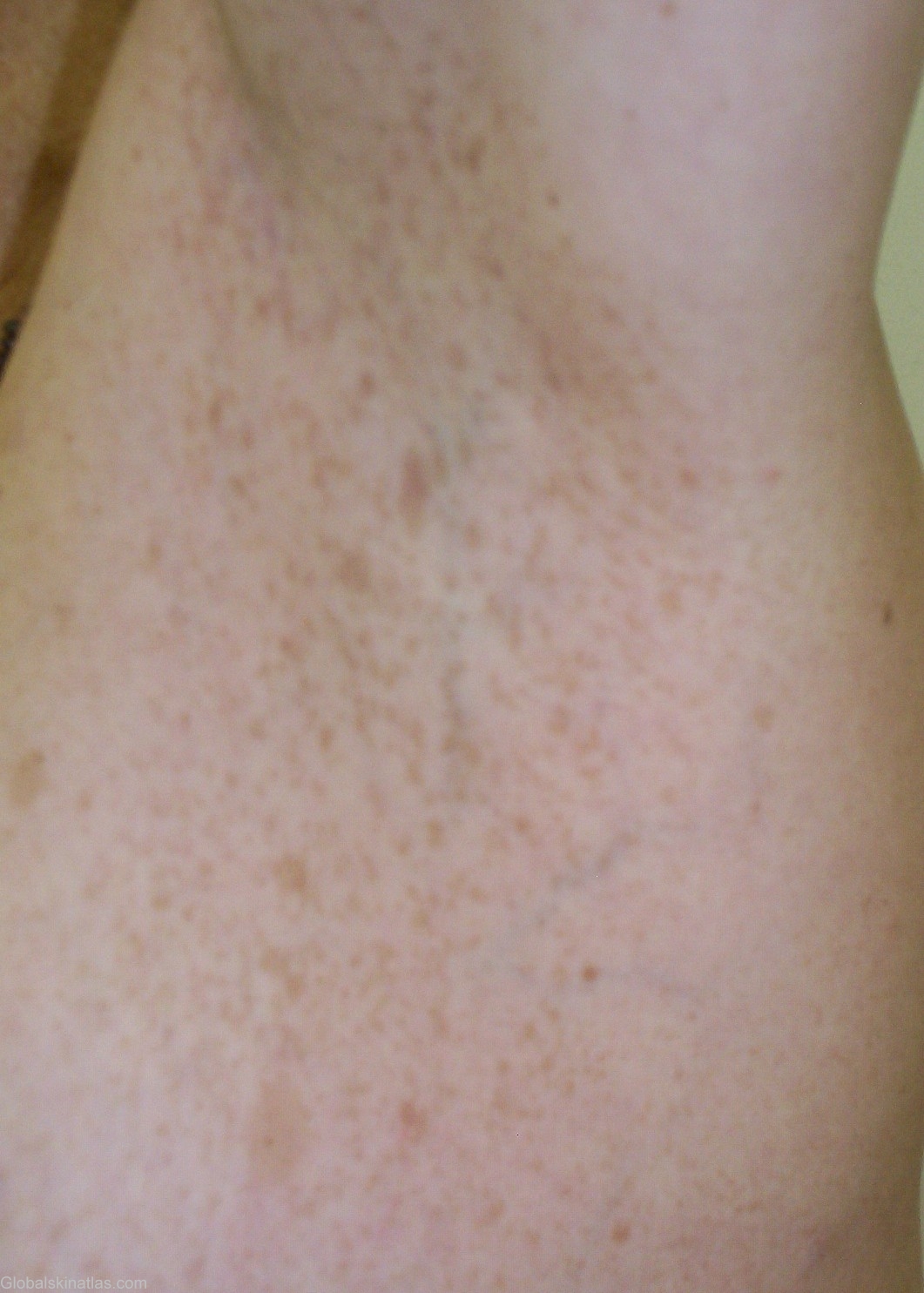
Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis
Description: Numerous small lentil-size brown macules (Crowe's sign)
Morphology: Macule brown
Site: Axillae
Sex: F
Age: 42
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Mehravaran Mehrdad
Differential DiagnosisHistory: Von Recklinghausen's disease, known also as neurofibromatosis type 1, is transmitted in autosomal-dominant fashion and is characterized by café au lait spots (usually patches), axillary or inguinal freckling, hamartomas of the iris (Lisch nodules), optic gliomas, and neurofibromas in the skin and in other organs. The gene for von Recklinghausen's disease has been mapped to a locus on chromosome 17q12. Axillary freckling is found in approximately 20% pf patients with neurofibromatosis. This finding is highly pathogonomic for neurofibromatsis. Lisch nodules are pigmented iris hamartomas, which were reportedly present in 94% of neurofibromatosis patients. Tumors associated with neurofibromatosis include neoplasms of neural origin include acustic neuroma, optic glioma, asterocytoma, ependymoma, spongioblastoma, meningioma and glioma of spinal cord. Schwannoma and neurofibrosarcoma. Extraneural malignancies include pheochromocytoma, Wilms’ tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma and leukemia. The other conditions that are frequently associated with neurofibromatosis can be categorized as neurologic, skeletal, endocrine, neoplastic, visceral, ans vascular abnormalities. Neurologic abnormalities include seizures, mental retardation, deafness, exopthalmos, macrocephaly, and speech impediments. Skeletal anbormalities include pseudoarthrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, short stature, and segmental hypertrophy secondary to the underlying plexiform neuromas. The most common endocrine abnormalities include precocious or delayed puberty and growth retardation. Thorough evaluation and close follow-up are necessory to detect and prevent complications such as bleeding and obstruction from visceral neurofibromas.