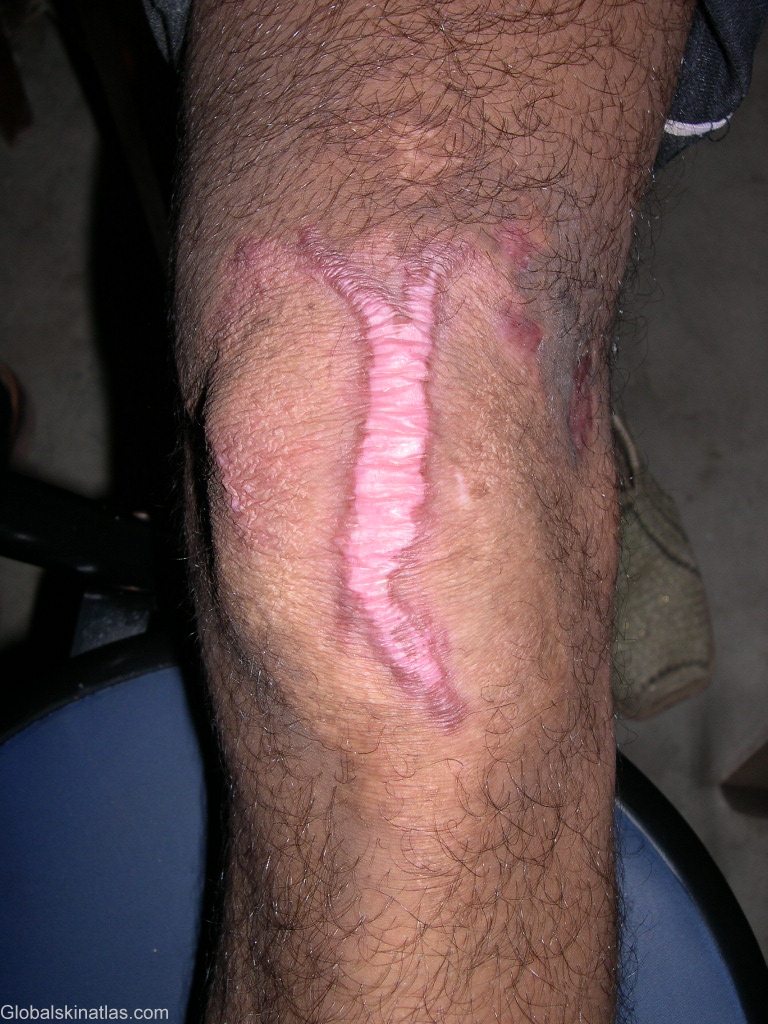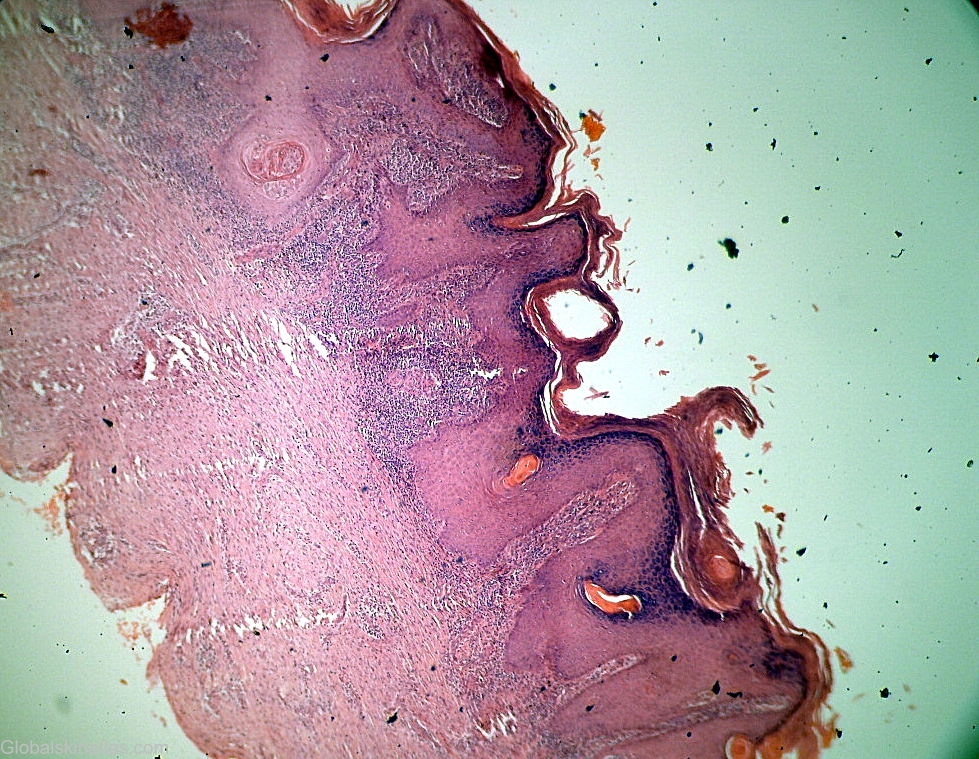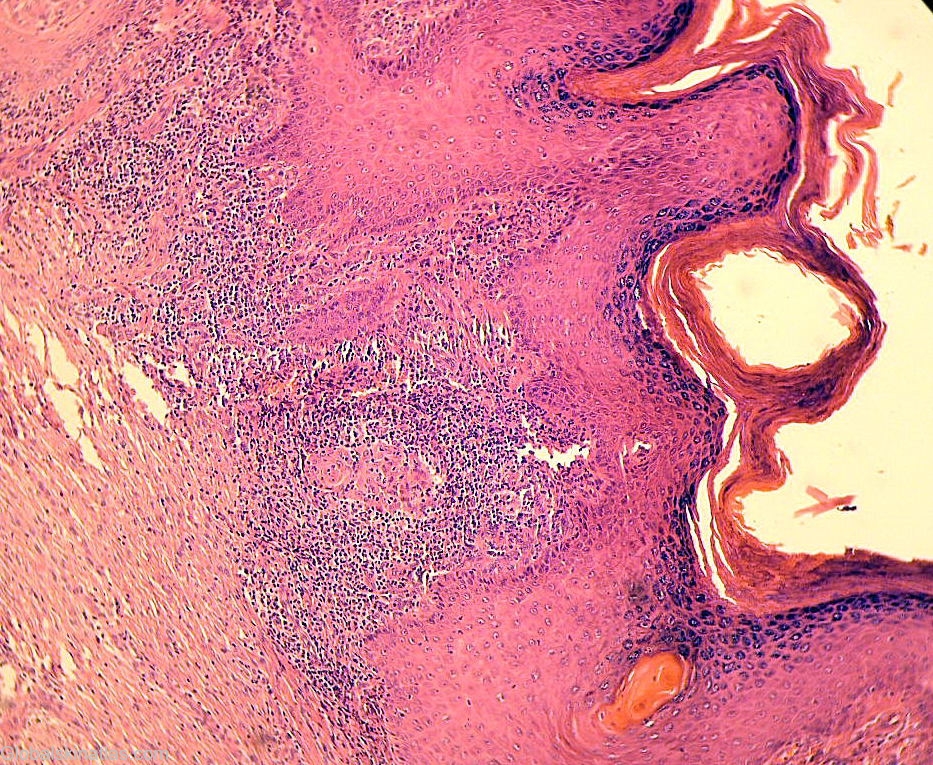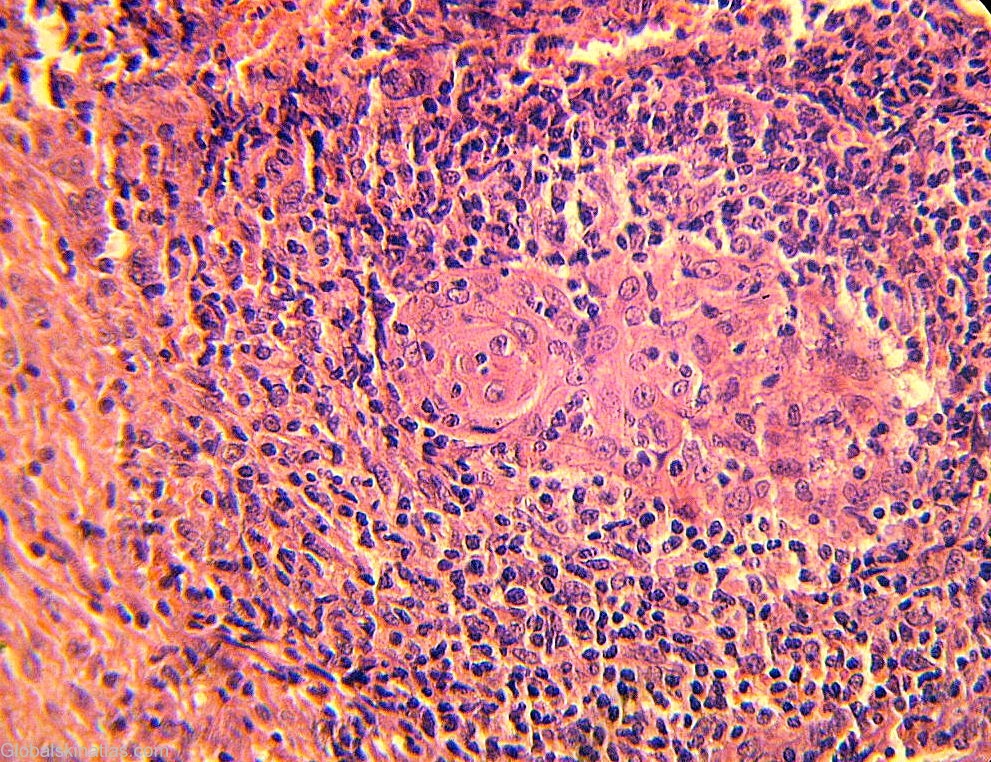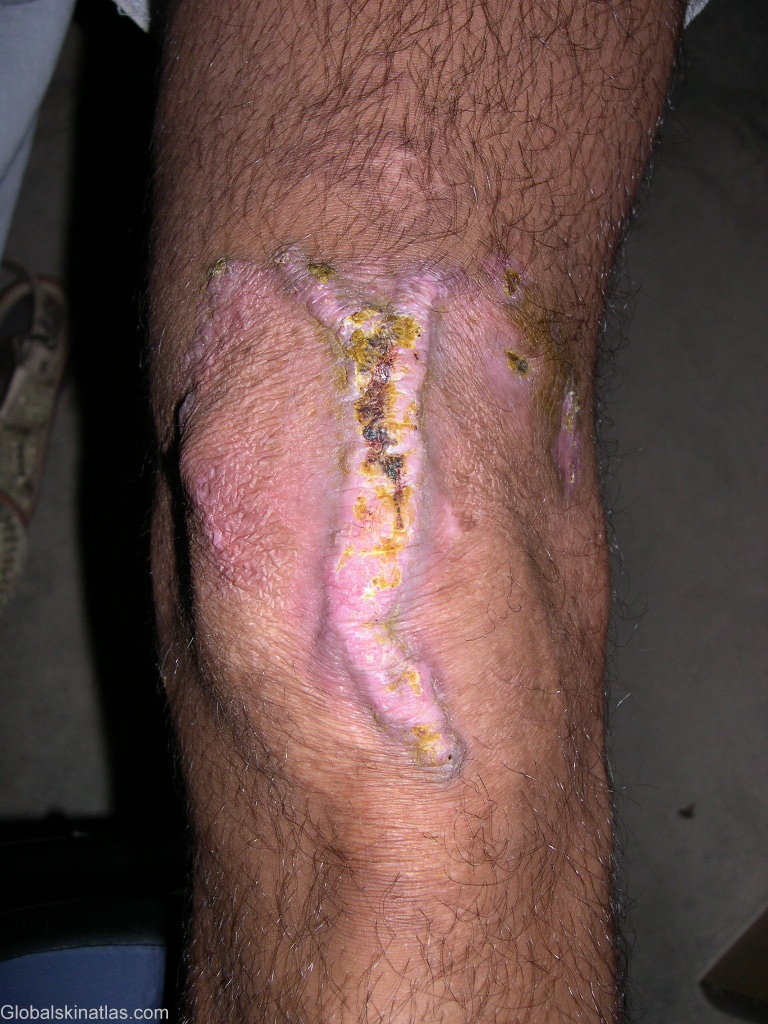
Diagnosis: Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis
Description: area after treatment
Morphology: Warty
Site: Knee
Sex: F
Age: 15
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Shahbaz Janjua
Differential DiagnosisHistory: Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis results from exogenous inoculation of M tuberculosis in a previously infected person who has a moderate or high degree of immunity. As trauma plays a role, the lesions are most common on the hands and feet. The lesion usually begins as a solitary papulonodule that progressively acquires a scaly, verrucous surface. Expansion of the lesion produces an annular, verrucous, red-brown plaque. Without therapy, tuberculosis verrucosa cutis follows a chronic course with central healing and centrifugal expansion. At its onset, tuberculosis verrucosa cutis frequently is mistaken for a common wart. Later in its course, the differential diagnosis includes the fungal infections blastomycosis and chromomycosis, as well as chronic vegetating plaques caused by infection with atypical mycobacteria. Histologically, tuberculoid granulomas with or without caseation are seen. Acid-fast bacilli often are present but rarely are numerous. Although the PPD test result is positive uniformly, it is important to note that it may also be positive in atypical mycobacterial infections.