
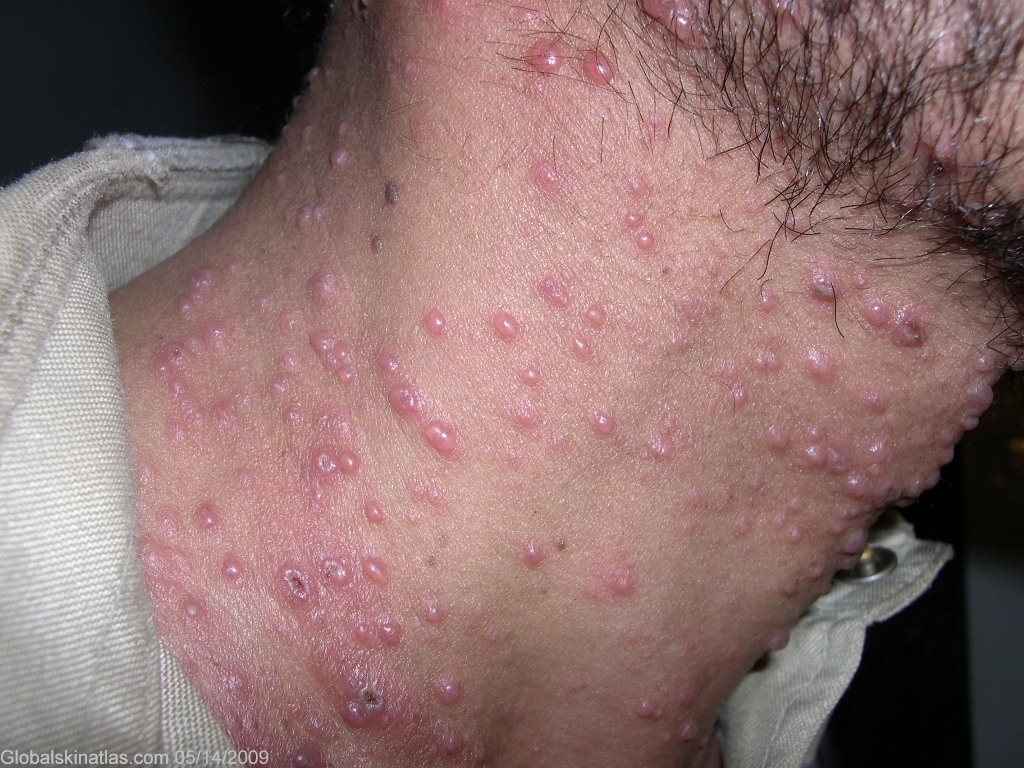
Diagnosis: Varicella
Description: Vesicles on an erythematous base
Morphology: Vesicles
Site: Neck side
Sex: M
Age: 38
Type: Clinical
Submitted By: Shahbaz Janjua
Differential DiagnosisHistory: Chickenpox (varicella) is an acute, contagious disease, characterized by a generalized exanthem consisting of vesicles that occur in successive crops and that rapidly evolves into pustules, crusts, and scabs. Chickenpox is a manifestation of primary infection with the varicella-zoster virus. The rash is characteristically centripetal, beginning on the face or scalp and spreading rapidly to the trunk, but with relative sparing of extremities. It begins as red macules but progress quickly to vesicles and crust. Itching is the rule. There is a tendency for new lesions to occur in crops. Most childhood infections are benign; however, the disease may have serious sequelae in adults. Pneumonia can complicate up to 20% of cases, with mortality rates reaching 40%. Other complications include encephalitis, myocarditis, pericarditis, adrenal insufficiency, glomerulonephritis, hepatic dysfunction, and thrombocytopenic purpura.